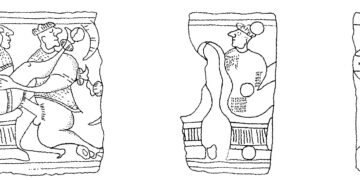
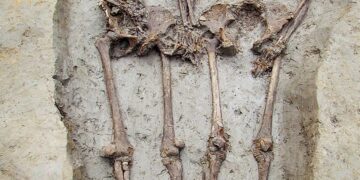
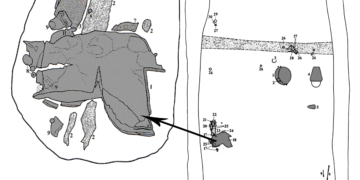
The development path leading to agriculture and animal husbandry started independently in several parts of the world. For us was most important the process that started some 13...
Read moreIt all started with wheat and barley. It was a process of intensification used to extract resources from the environment. The novelty developed in the near east spread...
Read moreSheep and goats were the first animals to be domesticated and formed together with pigs and later cattle the bases of the Neolithic pastoralist economy. Traditionally in the...
Read moreDuring the Early Bronze Age, we have witnessed in the Mediterranean a marked population increase that leads to the development of extensive settlements although the pattern of small...
Read moreThe impact of agriculture has been profound on humanity, most clearly in terms of population. This is because breeding plants and animals have significantly increased the availability of...
Read moreGenerally speaking, ancient civilizations gradually developed a more sophisticated economy following the creation of an agricultural surplus, population movement and urban growth, territorial expansion, technology innovation, taxation, the...
Read moreOne of the major technological inventions in antiquity, most probable derived from boat building technologies, was the discovery, that the wood can be bowed and bent if it...
Read moreAt the core of the concept, which was used in the last century to describe numerous two-handled ceramic vessels, are still Greek and Roman amphorae. They are pottery...
Read moreArchaeology is about facts – it focuses on the interpretations of material remains of ancient societies. However, sometimes these remains, especially those produced from organic materials; simply do...
Read moreMeals in the Mediterranean revolved in the last 10 millennia around the common staples of cereals, vegetables, fruit and olive oil – with an occasional bit of fish...
Read more